Data Sharing Between Apps
Method Registration
To expose a Glue42 method that can be invoked by other Glue42 enabled apps, you need to register the method in Glue42 and provide its implementation.
Registering Methods
To register a Glue42 method, first create a method instance using CreateServerMethod and then invoke Register on the created method instance.
Below is an example of a subroutine which registers a Glue42 method named "MyVBAMethod":
Dim WithEvents MyVBAMethod As GlueServerMethod
...
Public Sub RegisterMethod()
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
Set MyVBAMethod = Glue.CreateServerMethod("MyVBAMethod", "", "", "")
MyVBAMethod.Register
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
...
End SubMethod Implementation
The GlueServerMethod class exposes an event called HandleInvocationRequest. Provide a method implementation as its handler which will be executed when the registered method is invoked.
Below is an example of a subroutine handling an invocation request for a registered method.
Details about the example:
- the registered method accepts a composite value as an argument with the following structure represented in JSON format:
{
"operation": "AddSub",
"operands": [5, 3],
"metadata": {
"reason": "testing"
}
}the example demonstrates how to extract elementary fields from a composite value (see Accessing Composite Value Fields) and how to build a composite return value (see Building Composite Values);
the example demonstrates how to send a response to the caller by using
SendResultto send the return value to the caller andSendFailureto indicate failure and send an error message and an empty result value to the caller.
Private Sub MyVBAMethod_HandleInvocationRequest(ByVal request As IGlueInvocationRequest)
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
Dim Operation As String
Dim Operand_1, Operand_2 As Integer
Dim Reason As String
' Get the root of the composite argument.
Dim Args
Set Args = request.GetReflectData("")
' Extract the elementary fields from the composite argument.
Operation = Args("operation")
Operand1 = Args("operands")(0)
Operand2 = Args("operands")(1)
Reason = Args("metadata")("reason")
' Prepare the result as a composite value.
Dim Result
Set Result = Glue.CreateGlueValues
If Operation = "AddSub" Then
Dim ResultArray(0 To 1) As Integer
ResultArray(0) = Operand_1 + Operand_2
ResultArray(1) = Operand_1 - Operand_2
' Build the result as a composite value.
Result("resultArray") = ResultArray
Result("metadata")("info") = "Handled in VBA."
' Send the result back to the caller.
request.SendResult Result
Exit Sub
End If
HandleErrors:
' If an error occurs or "Operation" isn't recognised,
' send an error message and an empty result value.
request.SendFailure "Invalid argument(s) provided.", Glue.CreateGlueValues
End SubMethod Invocation
To invoke a Glue42 method, you need to obtain an instance of GlueMethodInvocator (proxy), build the argument values, initiate the invocation and provide a callback subroutine to handle the invocation result(s).
Invoking Methods
Below you can see examples of the steps you need to follow to invoke a Glue42 method. At the end of the section you can see a full method invocation example.
Method Invocator (Proxy)
Create a method proxy using CreateMethodInvocator. You can invoke a method multiple times reusing the same method invocator:
Dim WithEvents MyMethodProxy As GlueMethodInvocator
Public Sub InvokeMethod()
...
' Obtain a method invocator and reuse it for subsequent invocations.
If MyMethodProxy Is Nothing Then
Set MyMethodProxy = Glue.CreateMethodInvocator
End If
...
End SubBuilding the Argument Values
Build the arguments as a composite value (see Building Composite Values for details):
Public Sub InvokeMethod()
...
' Create an empty root value.
Dim Args
Set Args = Glue.CreateGlueValues
' Add the arguments.
Args("operation") = "AddSub"
Dim OperandsArray(0 To 1) As Integer
OperandsArray(0) = 5
OperandsArray(1) = 3
Args("operands") = OperandsArray
Args("metadata")("reason") = "testing"
...
End SubInvoking the Method
Use InvokeAsync or InvokeSync to initiate the method invocation.
Below is an example of using InvokeAsync to invoke the registered Glue42 method (for details about the provided arguments, see InvokeAsync):
Public Sub InvokeMethod()
...
MyMethodProxy.InvokeAsync "MyVBAMethod", "", Args, False, "", 3000
...
End SubBelow is a full invocation example:
Dim WithEvents MyMethodProxy As GlueMethodInvocator
Public Sub InvokeMethod()
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
' Obtaining a method invocator.
If MyMethodProxy Is Nothing Then
Set MyMethodProxy = Glue.CreateMethodInvocator
End If
' Building the argument values.
Dim Args
Set Args = Glue.CreateGlueValues
Args("operation") = "AddSub"
Dim OperandsArray(0 To 1) As Integer
OperandsArray(0) = 5
OperandsArray(1) = 3
Args("operands") = OperandsArray
Args("metadata")("reason") = "testing"
' Invoking the method.
MyMethodProxy.InvokeAsync "MyVBAMethod", "", Args, False, "", 3000
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
End SubTargeting
When invoking Glue42 methods, you can target a specific app (server) that has registered the method, a group of servers or the server that has registered the method first. Use the targetRegex and all parameters of InvokeAsync or InvokeSync to specify which servers to target:
targetRegex- optional regular expression pattern which allows selecting the target apps which will service the method invocation. If provided, only targets with app name matching the regular expression will be considered. An empty string orNothingwill match all app names;all- aBooleanvalue indicating whether the method invocation request should be sent to all available app targets or to one target only (the first that has registered the method);
You can use a combination of both parameters to filter the method servers you are interested in. Below is an example of invoking a registered method by targeting all apps with names that start with "clients":
Public Sub InvokeMethod()
...
MyMethodProxy.InvokeAsync "MyVBAMethod", "clients.*", Args, True, "", 3000
...
End SubHandling Invocation Results
InvokeSyncreturns the invocation results synchronously as аVBGlueInvocationResult.InvokeAsynchandles the invocation results with theHandleInvocationResultevent of theGlueMethodInvocatorinstance. Its handler is executed when the associated method invocation has completed (successfully or otherwise).
If you aren't interested in the invocation result, you still need to provide an empty implementation for the HandleInvocationResult event or, alternatively, declare the GlueMethodInvocator instance without WithEvents.
Below is an example of a subroutine handling an invocation result and demonstrating how to check the method invocation status and extract the return values:
- The instance of
IGlueInvocationResultpassed to the event handler has aResultsproperty which is an array ofVBGlueResultcontaining details about the invocation results. An array is used because the invocation request can be sent to multiple target apps at once. TheResultsarray always contains at least one element. - In the full invocation example the invocation request is sent to only one target app, therefore only one result is expected and extracted.
- The
Statusproperty of aVBGlueResultis aGlueMethodInvocationStatusenumeration value. - For details on how to extract data from composite values, see Accessing Composite Value Fields.
Private Sub MyMethodProxy_HandleInvocationResult(ByVal result As IGlueInvocationResult)
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
Dim ResultArr() As VBGlueResult
Dim FirstResult As VBGlueResult
' Get the first result.
ResultArr = result.Results
FirstResult = ResultArr(0)
If Not FirstResult.Status = GlueMethodInvocationStatus_Succeeded Then
' Handle unsuccessful invocation.
...
Exit Sub
End If
' Extract the result fields from the composite value.
Dim ResultArray
ResultArray = FirstResult.GlueData.GetReflectData("resultArray")
Dim AdditionResult, SubtractionResult As Integer
AdditionResult = ResultArray(0)
SubtractionResult = ResultArray(1)
' Do something with the result.
...
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
...
End SubDiscovery
Your app can discover registered Interop methods and streams and other apps (Interop servers) which offer them.
Listing All Methods & Streams
To find all registered Glue42 methods/streams, use the GetMethodNamesForTarget method and pass an empty string or Nothing as an argument:
Dim AllMethodNames() as String
AllMethodNames = Glue.GetMethodNamesForTarget("")Listing Methods & Streams for Target
To target a specific server or a group of servers for which to get all registered methods/streams, pass a regex value as an argument to GetMethodNamesForTarget:
Dim AllMethodNamesForTarget() as String
AllMethodNamesForTarget = Glue.GetMethodNamesForTarget("client.*")Listing All Interop Servers
To get a list of the names of all apps offering Interop methods/streams, use the GetTargets method:
Dim AllInteropServers() as String
AllInteropServers = Glue.GetTargets()Streaming
Overview
Your app can publish events that can be observed by other apps, or it can provide real-time data (e.g., market data, news alerts, notifications, etc.) to other apps by publishing an Interop stream. Your app can also receive and react to these events and data by creating an Interop stream subscription.
Apps that create and publish to Interop Streams are called publishers, and apps that subscribe to Interop Streams are called subscribers. An app can be both.
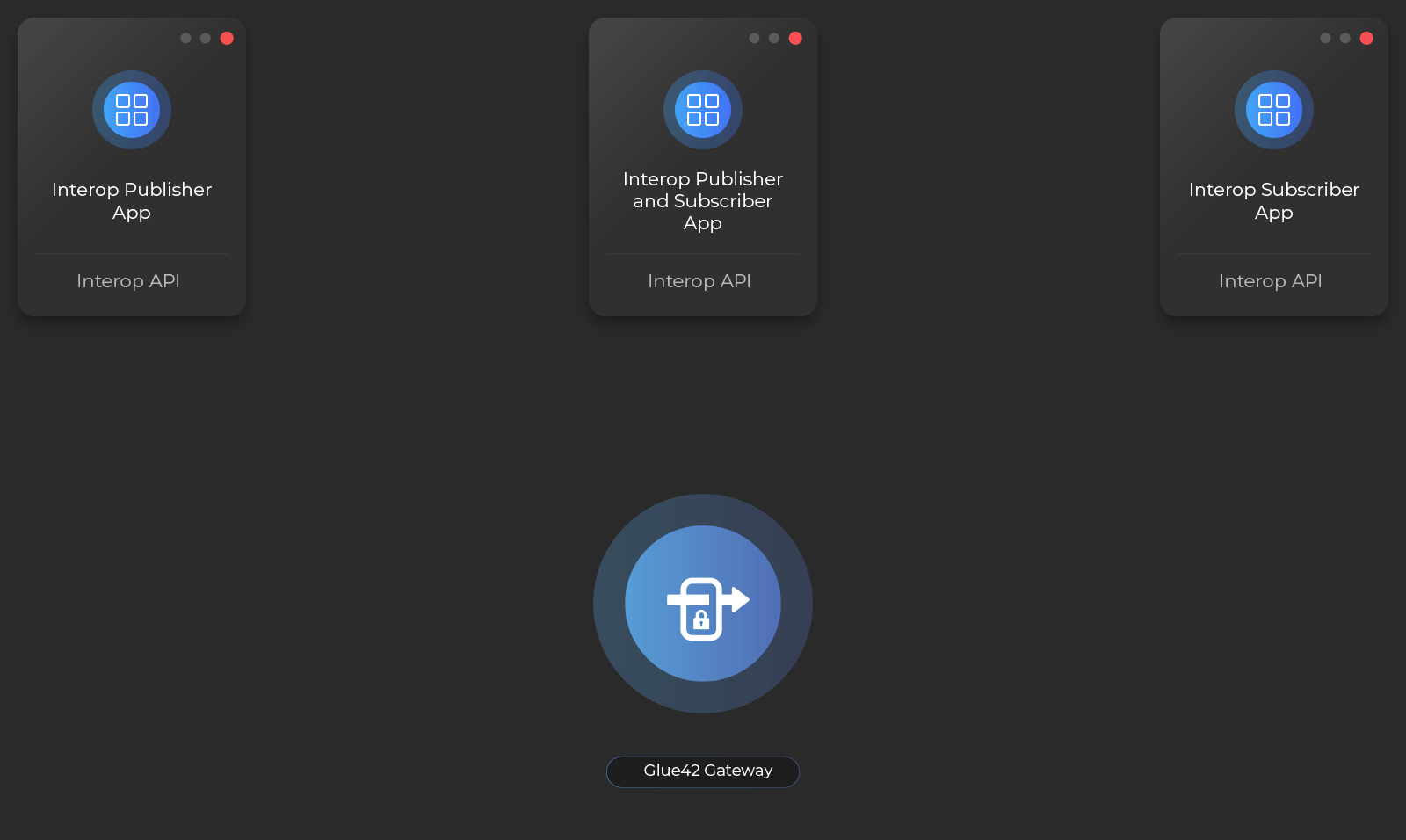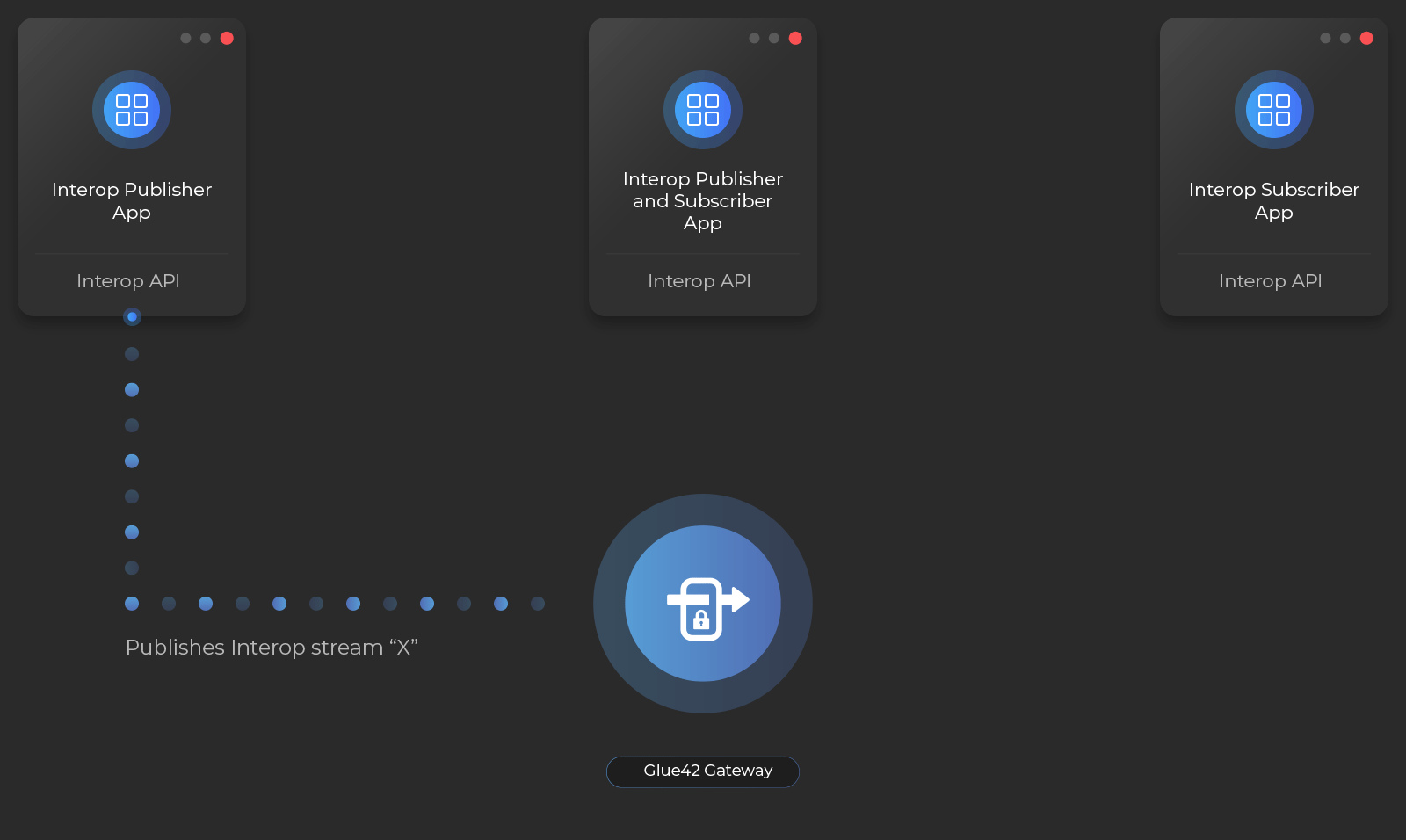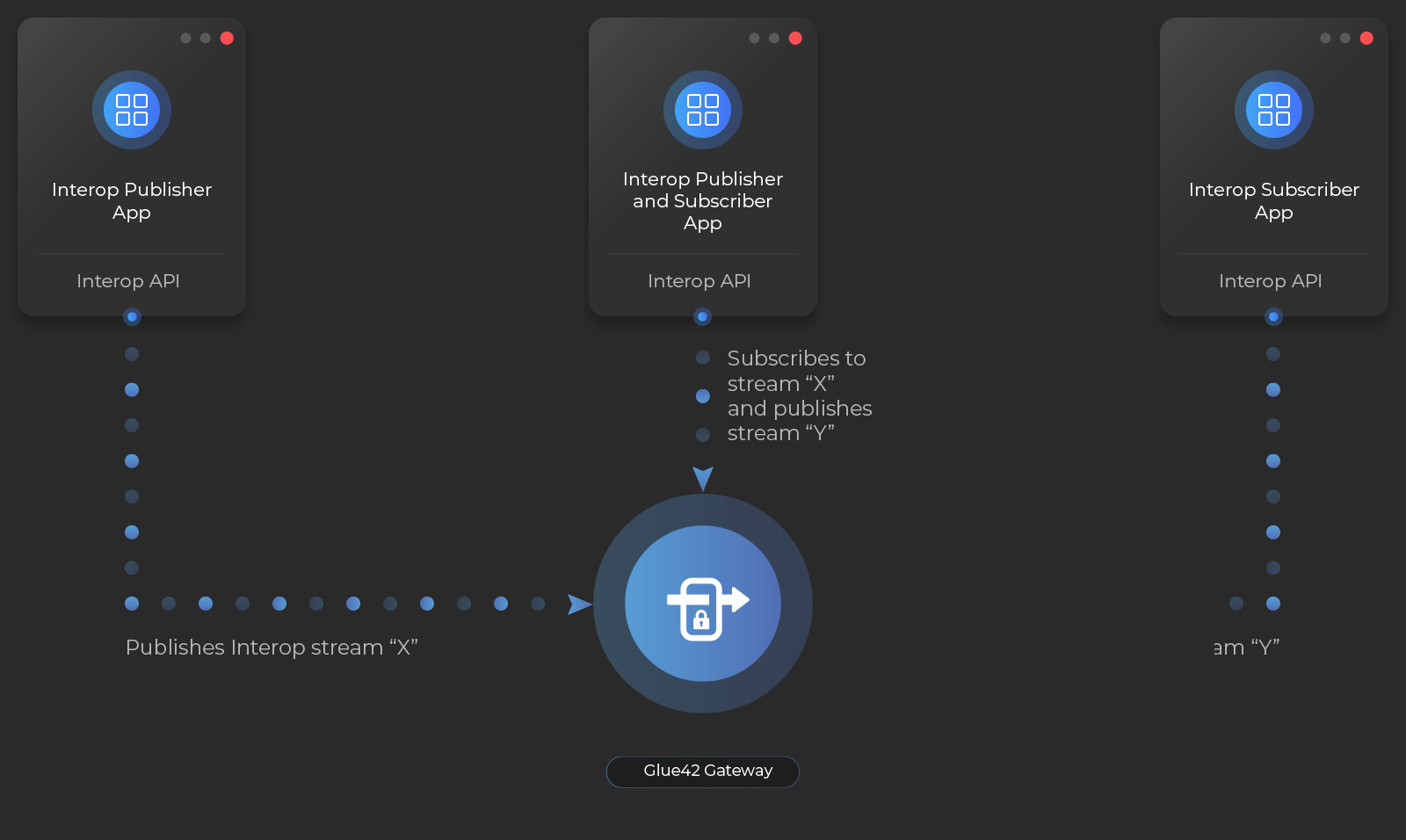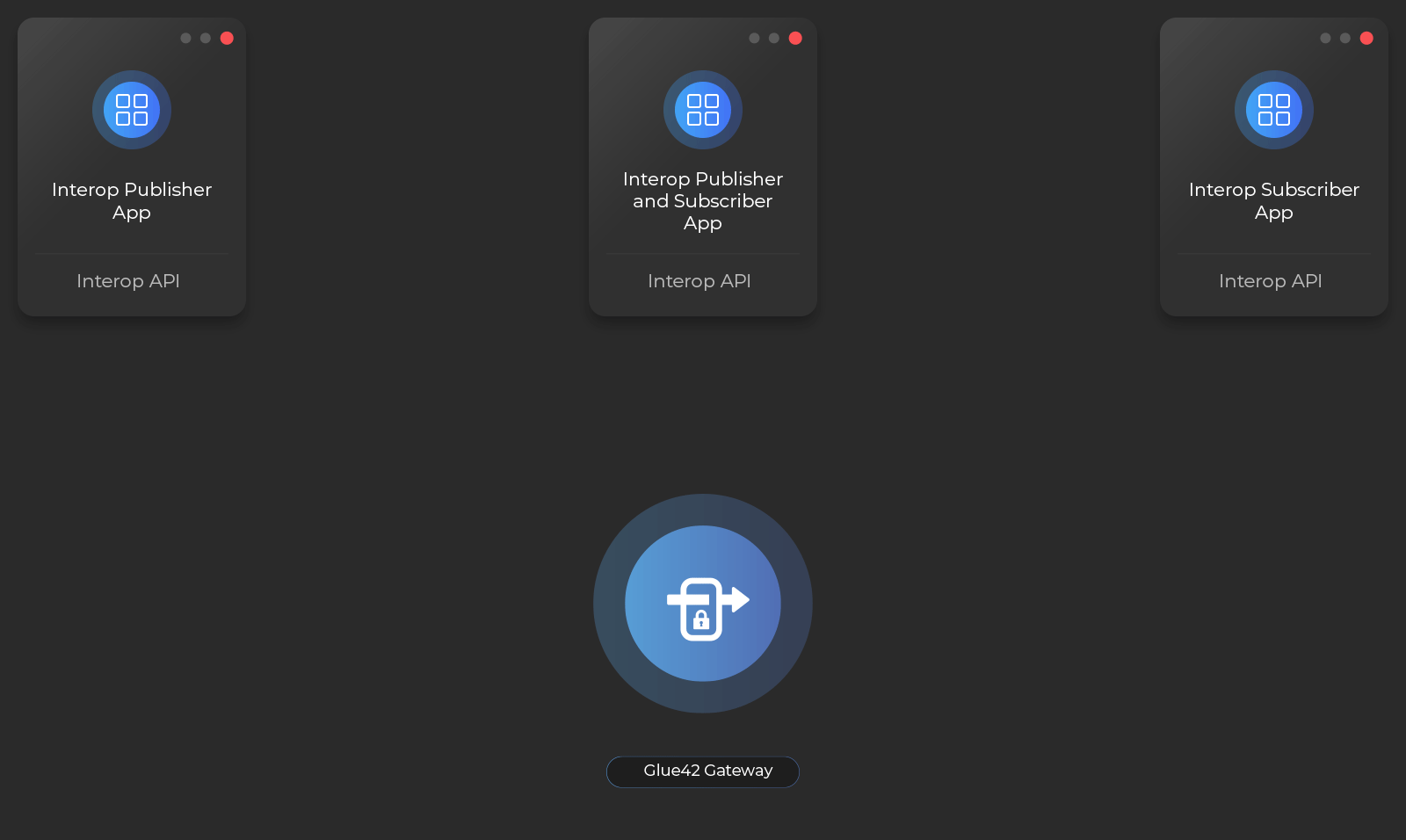
Interop Streams are used extensively in Glue42 Enterprise products and APIs:
- in Glue42 Windows - to publish notifications about window status change (events);
- in app configuration settings - to publish app configuration changes, and notifications about app instance state change (events);
- in the Glue42 Notification Service - to publish Notifications (real-time data);
- in the Window Management and App Management APIs (events);
Publishing Stream Data
To expose a data stream to which other apps can subscribe, you need to register a stream and provide implementations for handling the server side streaming events (subscription requests, added/removed subscribers). Once a stream has been successfully registered, the publishing app can start pushing data to it.
Creating Streams
Create a streaming method instance using CreateServerStream and invoke its Register method:
Dim WithEvents MyVBAStream As GlueServerStream
Public Sub RegisterStream()
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
If MyVBAStream Is Nothing Then
' The only required argument when creating a stream is a stream name.
Set MyVBAStream = Glue.CreateServerStream("MyVBAStream", "", "", "")
MyVBAStream.Register
End If
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
...
End SubAccepting or Rejecting Subscription Requests
GlueServerStream exposes an event called HandleSubscriptionRequest. Its handler is executed when an app attempts to subscribe to the stream. The handler receives a GlueSubscriptionRequest instance as an argument. You can use its GetReflectData method to extract the request arguments passed as a composite value by the subscriber. Use the Accept method of the request instance to accept the subscription on the default (unnamed) or a specific branch.
Below is an example of a subroutine handling a subscription request. The request is accepted or rejected based on the value of an argument that the subscriber has specified when sending the subscription request:
Private Sub MyVBAStream_HandleSubscriptionRequest(ByVal request As IGlueSubscriptionRequest)
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
' Extract the subscriber-defined `subscriptionCode` field from the request arguments.
Dim SubscriptionCode As String
SubscriptionCode = request.GetReflectData("subscriptionCode")
If SubscriptionCode = "rejectme" Then
' Reject the subscription request with a message.
request.Reject "Invalid subscription code."
Exit Sub
End If
' Accept the request on the default branch.
request.Accept "", Nothing
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
...
End SubAdded or Removed Subscriptions
Handling New Subscriptions
GlueServerStream exposes an event called HandleSubscriber. Its handler is executed when a new subscriber is added. The handler has two parameters - a VBGlueStreamSubscriber instance and a GlueData instance. The VBGlueStreamSubscriber instance contains information about the subscriber instance and you can use its Push method to send private data directly to it. The GlueData instance is a composite value that contains the subscription request arguments as specified by the subscriber.
Private Sub MyVbaStream_HandleSubscriber(ByVal subscriber As IVBGlueStreamSubscriber, ByVal requestData As IGlueData))
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
' Create a root composite value and add data to it.
Dim Data
Set Data = Glue.CreateGlueValues
Data("info") = "welcome"
' Push the data to the new subscriber.
subscriber.Push Data
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
...
End SubNote that new subscribers won't automatically get the data that has been previously published to the stream. This handler is the place where you can send private updates to the new subscriber, if necessary.
Handling Removed Subscriptions
GlueServerStream exposes an event called HandleSubscriberLost. Its handler is executed when an existing subscriber unsubscribes from the stream.
Below is an example of an empty handler subroutine:
Private Sub MyVBAStream_HandleSubscriberLost(ByVal subscriber As IGlueStreamSubscriber)
' Possibly handle the lost subscriber here.
End SubCancelling a subscription can be initiated either by the subscriber app or the stream publisher app. This handler is invoked in both cases. Handling this event can be useful if you want to record or propagate it. If this event isn't significant for the app, you must provide an empty handler subroutine.
Default Event Handlers
You may declare the GlueServerStream instance without WithEvents. In this case the Glue42 COM library will use the following default internal implementations:
HandleSubscriptionRequest- all subscription requests will be accepted on the default (unnamed) branch;HandleSubscriber- no operation;HandleSubscriberLost- no operation;
Pushing Data
You can push data to a stream by using the PushVariantData method of a GlueServerStream instance. Data can be sent to all subscribers on the stream, or to a group of subscribers on a specific stream branch.
The example below demonstrates how to push data to all subscribers on a stream:
' Create a composite value and add data to it.
Dim Data
Set Data = Glue.CreateGlueValues
Data("info") = "Data broadcast to all subscribers."
' Push data to all subscribers.
MyVBAStream.PushVariantData Data, ""You can also push data directly to a subscriber by using the Push method of a VBGlueStreamSubscriber instance (see Handling New Subscriptions).
Using Stream Branches
Using stream branches allows you to group subscribers by any criterion and target stream data at specific groups of subscribers. Branches are distinguished by their name (key). Each Glue42 stream has a default (unnamed) branch on which it accepts subscribers and to which it pushes data if no branch is specified.
To accept a subscription on a branch, specify the branch name when accepting the subscription. If the branch doesn't exist, it will be automatically created:
request.Accept "branch_01", NothingSee also Accepting or Rejecting Subscription Requests.
To push data to a specific branch, specify a branch name when pushing data to the stream:
Dim Data
Set Data = Glue.CreateGlueValues
Data("info") = "Data targeted at subscribers on branch `branch_01`."
MyVBAStream.PushVariantData Data, "branch_01"Consuming Stream Data
To receive data published on a Glue42 stream, an app has to create an instance of a GlueStreamConsumer, subscribe to a stream and provide the subroutines necessary for handling the incoming data and changes in the stream status.
Subscribing to Streams
Obtain a GlueStreamConsumer instance using CreateStreamConsumer, provide subscription arguments and send a subscription request using the Subscribe method of the GlueStreamConsumer instance. When the subscription request has been resolved or times out, the corresponding event handlers will be executed.
Dim WithEvents StreamConsumer As GlueStreamConsumer
...
Public Sub SubscribeToStream()
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
' Obtain a stream consumer instance.
If StreamConsumer Is Nothing Then
Set StreamConsumer = Glue.CreateStreamConsumer
End If
' Build the arguments to send with the subscription request.
Dim Args
Set Args = Glue.CreateGlueValues
Args("subscriptionCode") = "hello"
' Send the subscription request.
StreamConsumer.Subscribe "MyVBAStream", "", Args, False, "", 3000
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
...
End SubAs with invoking Interop methods, you can target specific servers providing the stream. See Targeting for more details.
Handling Subscriptions Client Side
Receiving Data
GlueStreamConsumer exposes an event called HandleStreamData. Its handler is executed when a stream publishing app pushes data to the stream. The handler accepts two parameters - a GlueMethodInfo instance containing information about the stream, and a GlueData instance containing the data pushed to the stream.
Below is an example of a subroutine handling incoming data from a stream:
Private Sub StreamConsumer_HandleStreamData(ByVal stream As IGlueMethodInfo, ByVal data As IGlueData)
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
' Extract information about the data publisher.
Dim StreamName as String
Dim ApplicationName as String
StreamName = stream.method.Name
ApplicationName = stream.method.Instance.ApplicationName
' Extract data from the composite value.
Dim Info As String
Info = Data.GetReflectData("info")
' Do something with the data.
...
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
End SubSubscription Activated Handler
GlueStreamConsumer exposes an event called HandleSubscriptionActivated. Its handler is executed when a subscription request has been dispatched to Glue42. The main purpose for handling this event is to provide an instance of the GlueStreamSubscription which the app may later use to unsubscribe from the stream. To unsubscribe from the stream, use the Close method of the subscription instance.
Below is an example of a subroutine handling the event:
Dim StreamSubscription As IGlueStreamSubscription
Private Sub StreamConsumer_HandleSubscriptionActivated(ByVal subscription As IGlueStreamSubscription)
' Keep a reference to the subscription instance.
Set StreamSubscription = subscription
End SubStream Status Handler
GlueStreamConsumer exposes an event called HandleStreamStatus. Its handler is executed when the GlueStreamState of the associated stream subscription changes.
Below is an example of a subroutine handling the event:
Private Sub StreamConsumer_HandleStreamStatus(ByVal stream As IGlueMethodInfo, ByVal state As GlueStreamState, ByVal Message As String, ByVal dateTime As Double)
On Error GoTo HandleErrors
Select Case state
Case GlueStreamState_Pending
' Subscription request is pending.
...
Case GlueStreamState_Opened
' Subscription request has been accepted.
...
Case GlueStreamState_Closed
' Subscription has been closed.
...
End Select
Exit Sub
HandleErrors:
' Handle exceptions.
End SubYou may provide an empty implementation if you aren't interested in performing any actions when the stream subscription status changes.
Stream Closed Handler
GlueStreamConsumer exposes an event called HandleStreamClosed. Its handler is executed when the stream is closed and the associated stream subscription has been terminated.
Here is an example of a subroutine handling the event:
Private Sub StreamConsumer_HandleStreamClosed(ByVal stream As IGlueMethodInfo)
' Perform actions when the stream is closed.
...
End SubYou may provide an empty implementation if you aren't interested in performing any actions when the subscription has been terminated.
